Fish Farming is a type of aquaculture that raises fish in fish tanks and sells them as food. This is the fastest-growing segment of animal feed production. About half of the fish consumed worldwide today are raised in these artificial environments. Commonly farmed species include salmon, tuna, cod, trout, and halibut. These ‘aqua farms’ can take the form of wire cages submerged in natural bodies of water or concrete enclosures on land.
Fish farming or fish farming is the process of raising, rearing, and transporting fish for domestic and commercial purposes. Fish is high on the list as a healthy and nutritious food choice as it is a rich source of protein and other minerals.

However, there are three main types of fish farming. They are monoculture, polyculture, and monosex culture.
To define fish farming, we first need to familiarize ourselves with its variants. let’s start!
Table of Contents
- Types of Pisciculture
- Benefits of Fish Farming
- Species of Fish
- Importance of Fish
- Setting up a Fish Farming Business
- Preparing a Fish Pond
- Fish Breed Selection
- Fish Feeding and Maintenance
- Further Readings: Relevant Articles
- FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
Types of Pisciculture
There are three main types of fish farming available with a wide variety. these are:
Monoculture
This system allows the breeding of a single species of fish. It offers high productivity & quality and is very popular among consumers. In India, shrimp is typically an example of monoculture fish.
Polyculture
Also called combined or mixed farming. Polyculture allows different compatible species of fish to be kept in a common pond. However, different species must have different eating habits to survive different diets from a common resource. It is a useful method of fish farming.
Monosex Culture
In general, this culture allows the breeding of female or male fish of the species. This is how fish are obtained through this culture. An example of such a fish is tilapia.
Now let’s understand the Fish Farming in detail:
Fish Farming Methods
Different fish farms use different methods. Following are some of the fish farming methods:

Cage System
Metal cages are submerged in water containing fish. In this type of marine aquaculture, fish can be artificially fed.
Pond System
This system requires a small pond or aquarium to grow the fish. This is one of the most profitable fish farming techniques as it uses water containing fish waste as fertilizer in the agricultural field.
Integrated Recycling System
This method uses large plastic tanks with fish in a greenhouse. There is also a hydroponic bed next to the tank. I grow herbs such as basil and parsley in aquarium water.
Classic Fry Farming
With this technology, fish are raised from eggs to seedlings. They are then released into river water.
Benefits of Fish Farming
Following is the list containing the advantages of fish farming:
- Fish farming does not require many resources. For starters, a small concrete tank will suffice.
- Farmed fish are grown under controlled conditions to enhance their nutritional value. Therefore, the quality of these fish is superior to wild fish.
- There are many species of fish suitable for breeding. This allows fishery owners to choose the best fish species that will bring them a profit. People can make money by turning poor and barren land into fishponds.
- The demand for fishing is increasing day by day. Therefore, people can start fish farming by allocating space in existing fish farms which increases their income.
- Fish farming has fewer risk factors because the fish are kept in cages. This prevents outsiders from entering the area and catching fish.
- Aquarium fish are safe, so there is no need to catch wild fish in large numbers. Helps restore natural ecosystems.
- Another important aspect of aquaculture is job creation.
Species of Fish
Following are some of the most common species of fish that are raised on fish farms:
Cat Fish Farming
Catfish thrive in warm climates. Catfish are mainly raised in freshwater ponds and feed mainly on soybeans, corn and rice. Catfish are often considered one of the sustainable fish species suitable for farming. Catfish farming began in his 1900s and was commercialized in the 1950s. Catfish are very popular due to their health benefits and market demand. Farmed catfish are typically harvested at 18 months of age, while wild catfish are typically much larger. There are many species of catfish, but the three most popular are blue catfish, channel catfish and flathead catfish.
Tilapia Fish Farming
Tilapia is the third most popular fish used in aquaculture and aquaculture, the first two he being carp and salmon. They are growing in popularity due to their high protein content, large size and ability to grow. Tilapia is a tropical fish that needs warm water to survive. The ideal water temperature is usually 28-30°C. Tilapia fish are known to reproduce rapidly, which presents a challenge in managing agricultural tilapia fish species. If fish are not treated properly, they can compete fiercely for food and stunt their growth. Tilapia is disease and parasite resistant. Tilapia farming originated in Africa and is popular in Honduras, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines and Indonesia. Tilapia fish require a grain-based diet and will not eat other fish, but he is also considered one of the most invasive fish species.
Salmon Fish Farming
Salmon is one of the most popular fish species and the most commonly farmed is Atlantic he salmon. Two other types of farmed Pacific salmon are he, Chinook and Coho. Farmed salmon are vaccinated to prevent disease outbreaks and rarely require additional medication. I am often asked about the color difference between wild and farmed salmon. Farmed salmon is not colored. Salmon bait helps protect wild fish stocks
Tuna Fish Farming
Tuna is a saltwater fish and plays an important role in commercial aquaculture. Japan is the largest consumer of tuna and has invested a significant amount of research into fish research. There are several types of tuna, including bluefin tuna, yellowfin tuna, and albacore tuna. Tuna farming is complicated by the fact that the fish are “giant” and very active, making it very difficult to simulate the natural environment. Most tuna for human consumption is wild-caught and raised in facilities designed to increase weight gain. Tuna is carnivorous and eats other fish. Tuna is typically farmed in offshore pens and sometimes in recirculating systems.
Eel Fish Farming
Eel farming began in the early 1950s and he is considered one of the most profitable fisheries in terms of export value. However, the return value is mainly driven by the Asian market and varies by culture. Eels are carnivorous, catadromous fish. In other words, eels live in freshwater when young, but when they mature they migrate to the sea to breed, spending 8 to 30 years in freshwater before migrating. Most eel farming takes place in Asia, with China, Japan and Taiwan being the largest producers. Glass eels are preferred over glass eels as they are easier to transport and more adaptable to artificial feeding. Eel farming can take one of two different forms he of high-intensity recirculating tanks (indoor) or concentrated pond systems.
Importance of Fish
Fish are an essential food source for humans. According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) (1997), it is the single most important human source of high-quality protein, providing approximately 16% of the animal protein consumed by the world’s population.
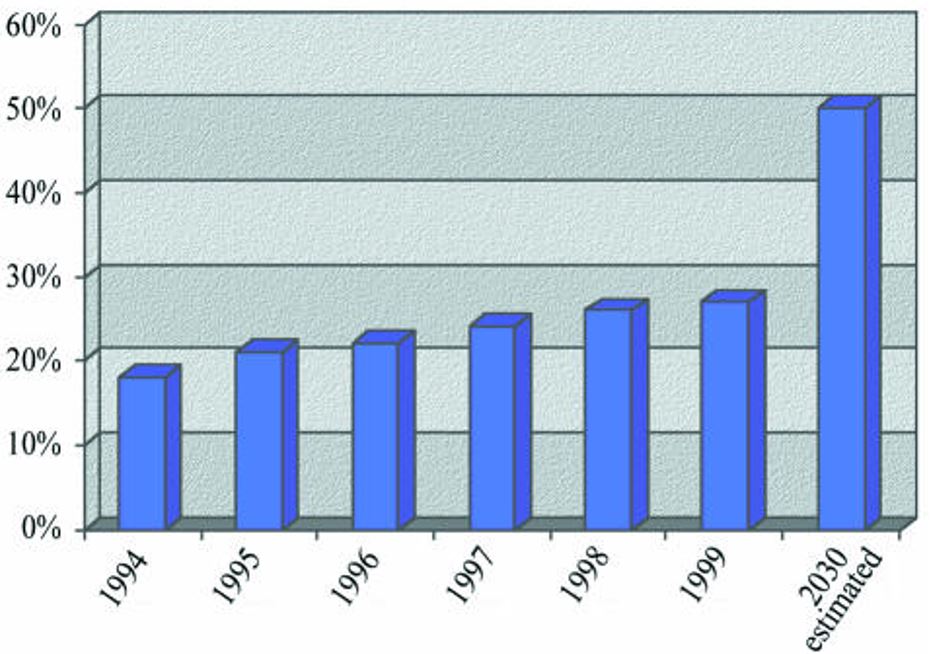
It is a particularly important source of protein in areas where livestock are relatively scarce. Less than 10% of the animal protein consumed in North America and Europe comes from fish, compared to 17% in Africa, 26% in Asia, and 22% in China (FAO, 2000). FAO estimates that around 1 billion people worldwide depend on fish as the main source of animal protein (FAO, 2000).
Figure shows the year-wise percentage of total food fish in aquaculture.
Setting up a Fish Farming Business
Starting a fish farming business is not that easy. For setting up a profitable fish farming business, you have to go through some procedures. We have described various steps of fish farming.
Preparing a Fish Pond
The main infrastructure of a fish farming business is a pond. Without ponds, commercial aquaculture is not possible. You can use an existing pond or create a new pond for your Indian fishmonger. You can keep fish in both seasonal and permanent ponds. When raising fish in ponds where there is no water all year round, it is necessary to raise fast-growing or early-ripening fish. Before you put minnows in your pond, prepare them properly. Clean the bottom of the pond and then apply fertilizer. Optimizes the PH value of pond water and soil. A quality pond environment ensures high production and high profitability. Check out our complete pond management system.
Fish Breed Selection
Fish species selection plays an important role in the sustainability of our business. Decisions should be made based on market demand, maintenance perspective, resource availability, resource efficiency, etc. Carp items such as katra, loaf, grass carp and carp are suitable for Indian ponds. Other varieties such as tilapia, catfish are also grown in Indian ponds. Polyculture (in the same pond he keeps two or more species of fish) is a good strategy for optimal utilization of resources. Good quality seedlings (fry) are available from your local aquaculture company or fisheries department.
Fish Feeding and Maintenance
Particular attention should be paid to fish breeding. The pH of the water should be between 7 and 8 for optimal growth. A possible virus attack should be avoided. Fishponds should be protected from predators. Daily reconnaissance should be carried out and suspicious fish should be isolated from the pond to prevent disease from spreading throughout the pond. Fish diseases can be treated by treating the water with salt, potassium permanganate solution, chemicals, etc.
Local markets are the most accessible markets for the majority of farmers. But the profit will be less compared to export. Fish meat can be processed into value-added products and exported to overseas markets. Establishing farmers’ unions can help with this marketing. The advantage of local markets is that selling fish is not a problem here and farmers can earn a decent income. Thus, the strengths of both markets ensure the success of this farming. . Fish farming is becoming one of the most important agricultural sectors to alleviate unemployment problems in rural areas. So fish lovers always have a chance.
Further Readings: Relevant Articles
Click on the below links to read about Bamboo Farming.
Types of Bamboo
Life of Bamboo
Bamboo Farming in US (United States)
Bamboo Farming in India
National Bamboo Mission in India
Diseases in Bamboo
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
What is fish farming called?
aquaculture, also called fish farming, fish culture, or mariculture, the propagation and husbandry of aquatic plants, animals, and other organisms for commercial, recreational, and scientific purposes.
What are the 3 types of fish farming?
Types of fish farming systems
- Integrated Recycling System: Completely closed system.
- Flow-through/raceway: Semi-closed system.
- Floating cage system: Open system.
Is fish farming sustainable?
As in the United States, responsibly practiced aquaculture is increasingly recognized as one of the greenest ways to produce food and protein.
What do farmed fish eat?
Farmed fish are fed diets specifically designed to meet their nutritional needs. This feed contains all the essential nutrients they need to maintain their health and growth. This food usually comes in the form of dry pellets and is similar in many ways to dry dog food.
What is the history of fish farming?
Fish farming is an ancient practice dating back to around 2500 BC. In China, carp were cultivated in flooded ponds and artificial lakes.
Are fish farms profitable?
Yes, aquaculture can be profitable if the farmer has the right natural resources, good management skills and enough capital to invest in the business



