A Bitcoin halving (also known as a “halvening”) is an event in which the reward for mining new blocks is halved. In other words, a miner receives 50% bitcoins for verifying a transaction. Bitcoin halvings are scheduled every 210,000 blocks (approximately every four years) until the network generates a maximum supply of 21 million Bitcoins.
Bitcoin Halving is an important event for traders as it reduces the number of new Bitcoins generated by the network. This limits the supply of new coins, so if demand remains strong, the price could rise. This happened in the months before and after the previous halving, which caused the price of Bitcoin to rise rapidly, but the situation is different from halving to halving, and demand for Bitcoin can fluctuate greatly.
Bitcoin’s anonymous inventor Satoshi Nakamoto used his infinite wisdom to determine that there were only 21 million BTC. They wanted the new coin to be issued in phases, but at the same time, it was important that a large amount of bitcoin sooner or later circulated.
So how does the Bitcoin halving work? When the cryptocurrency was first launched, miners received 50 BTC per block. In this way, the early adopter has lured into mining the network, before it became clear how successful it would be. The rate at which new bitcoins were created was halved every 210,000 blocks mined. That means it will halve roughly every 4 years until all 21 million Bitcoins are mined.
According to the Bitcoin halving history, the last three halvings were in 2012, 2016, and 2020. The first Bitcoin halving (Bitcoin split) occurred in 2012 when the reward for mining blocks was lowered from 50 BTC to 25 BTC.
The 2016 halving reduced the incentive to 12.5 BTC per block mined, and as of May 11, 2020, each newly mined block will only generate 6.25 BTC. The next Bitcoin halving is scheduled for 2024. This halving system will last until about 2140.
Table of Contents
- Why Bitcoin halving is important?
- How Many Bitcoin Halvings Have There Been Before?
- What is Bitcoin halving and how does Bitcoin halving work?
- Why does Bitcoin halving occur?
- Implications of the Bitcoin halving event
- When is the next Bitcoin halving event?
- Summary:
- Further Readings:
- FAQs
Why Bitcoin halving is important?
A Bitcoin halving usually comes with a lot of cryptocurrency turmoil. As a result of the halving, the supply of available bitcoin has decreased and the value of bitcoin that has not yet been mined has increased. And with such change comes an opportunity to take advantage of it.
The first halving occurred on November 28, 2012, when the price of BTC was around $12. A year later, Bitcoin has risen to almost $1,000. The second halving occurred on July 9, 2016, after which Bitcoin price plummeted to $670 before rising to $2,550 by July 2017. Bitcoin hit a record high of around $19,700 in December of that year. Bitcoin’s price hit $8,787 during its final halving in May 2020 and exploded in the months that followed.
| Halving Year | BTC Per Block Before Halving | BTC Per Block After Halving | Price on Halving Day | Price After 150 Days |
| Year 2012 Halving | 50 BTC | 25 BTC | $ 12.35 | $ 127.00 |
| Year 2016 Halving | 25 BTC | 12.5 BTC | $ 650.53 | $ 758.81 |
| Year 2020 Halving | 12.5 BTC | 6.25 BTC | $ 8821.42 | $ 10,943.00 |
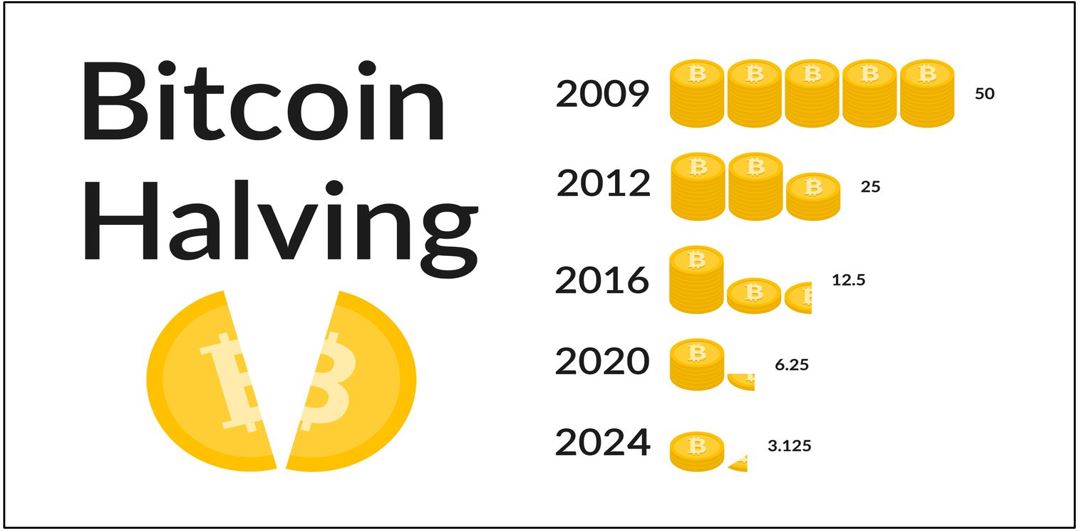
Image Source: https://www.investopedia.com/bitcoin-halving-4843769
Of course, there were other factors to consider when analyzing the post-halving Bitcoin boom.
- Press coverage of Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies.
- The attraction of anonymity in digital assets.
- There is a gradual increase in the number of practical use cases for the currency.
But if we believe history’s worth, past Bitcoin halvings have been a long-term bullish engine for cryptocurrency prices. Meanwhile, the third halving of Bitcoin’s existence will almost certainly affect the BTC ecosystem in a number of ways. The number of Bitcoin miners is expected to decline as it becomes unprofitable for Bitcoin.
Bitcoin halvings regularly symbolize Bitcoin’s deflationary tendencies. This has been at the center of the bullish case since Bitcoin’s inception. That said, Bitcoin as a decentralized cryptocurrency cannot be forgotten by governments and central banks, and the total supply is in full control.
How Many Bitcoin Halvings Have There Been Before?
The first-ever Bitcoin Halving took place on November 28, 2012, with the reward reduced to just 25 BTC. On that day, 1 BTC will result in a difference of about $12. But look where a year from now. A quick look archive shows that in 2013, the price of Bitcoin on that day was $1,031.95. That’s an annual return of 8,500%, a return that would stun most Wall Street investors.
Let’s go back to 2016 when rewards threatened to drop again, this time back to 12.5 BTC. The day Bitcoin hit 420,000 blocks, July 9th to be exact, the coin price was $650.96. A year later, Bitcoin already at $2,518.44. However, the actual Ascension occurred five months later than March 12th. Bitcoin soared to an all-time high of $20,089 on October 17, 2017. It took just 526 days to achieve 2,990% growth.
It is not an exaggeration to say whether or not this halving will continue to grow as the previous halving has yet to be determined. Either way, it will be 12-18 months before we know if Bitcoin can make a comeback.
What is Bitcoin halving and how does Bitcoin halving work?
To understand how Bitcoin halving works, we first need to understand the basics of how cryptocurrencies are created.
Bitcoins are created by a decentralized system where people known as miners use powerful computer systems to solve cryptographic puzzles and verify and verify transactions on the Bitcoin ledger known as the blockchain. In return, they receive rewards in the form of newly created Bitcoins.
Bitcoin mining is a kind of competition. Miners basically compete to be the first to add new blocks to the blockchain. For each block added, you will receive a certain number of new Bitcoins as a reward. The creators of Bitcoin programmed the block reward to halve periodically.
The reward for mining blocks is halved for every 210,000 blocks added. Currently, it takes about four years to add that many blocks, so Bitcoin halvings occur about every four years. The last time and third half-life took place were in May 2020. The next one is scheduled for 2024.
In theory, after 21 million Bitcoins, no more will be generated.
“Just like the amount of gold on earth is finite, the amount of bitcoin is limited to 21 million,” said Buchi Okoro, CEO of African cryptocurrency exchange Quidax. “Bitcoin can be thought of as a natural resource for the Internet, which is why it is called ‘digital gold.’”
Why does Bitcoin halving occur?
Bitcoin mining algorithms are programmed to look for a new block every 10 minutes. The time it takes to find a block will decrease as more miners join the network and add more hashing power. Mining difficulty resets approximately every two weeks to recover the 10-minute goal. The average time to find a block has consistently remained below 10 minutes (about 9.5 minutes) as the Bitcoin network has grown dramatically over the last decade.
Bitcoin supply is limited to 21 million units. Once the total reaches 21 million, the new BTC generation will stop. Bitcoin halving ensures that the amount of Bitcoin that can be mined in each block decreases over time, making BTC scarcer and more valuable.
Logically, the incentive to mine Bitcoin decreases with each halving. On the other hand, the Bitcoin halving has been associated with a large spike in the BTC price, giving miners an incentive to mine more even if their payouts are halved.
Bitcoin miners are encouraged to continue mining as the price increases. On the other hand, if the price of digital currency does not rise and block rewards decrease, miners may lose the incentive to create more Bitcoins. This is because mining Bitcoin is a slow and expensive process that requires a lot of computer processing power and electricity.
Implications of the Bitcoin halving event
In the broader sense of the halving, lower Bitcoin mining rewards reduce the amount miners earn by adding new transactions to the blockchain. Miner rewards determine the flow of new Bitcoins in circulation. As a result, halving these payments would reduce the influx of new Bitcoin. This is where the economics of supply and demand come into play. As supply decreases, demand fluctuates (increases or decreases), resulting in price changes.
Bitcoin’s inflation rate also decreased due to the halving. Inflation is the loss of purchasing power of something, in this case, a currency. However, Bitcoin’s basic infrastructure is designed to be a deflationary asset. To achieve this, half-life plays an important role.
Bitcoin inflation was 50% in 2011, but after the halving in 2012, it plummeted to 12% in 2012 and 4-5% in 2016. The current inflation rate is 1.77%. This means that the value of Bitcoin increases with each halving. All halving events have historically resulted in Bitcoin bull markets. When supply decreases, prices & demand increase. However, this uptrend will not happen immediately.
Due to the high cost of electricity to run computers that solve math puzzles, the price of BTC will have to rise significantly for miners to get half the coin. Miners will find it difficult to stay competitive and stay in business if their rewards decline and prices do not rise at the same time.
Miners should be as efficient as possible. Therefore, we need new technologies that can generate more hashes per second while using less energy and reducing overhead.
In addition, there are signs of interest in the currency from several countries, whose economies could affect Bitcoin’s price. More importantly, Bitcoin’s price is likely to rise due to its current rise in awareness. Transaction volumes will only increase as more businesses, small businesses, and even major institutions join Bitcoin and the blockchain.
When is the next Bitcoin halving event?
Over 18.5 million, or almost 89% of the 21 million BTC that could ever exist, have been mined and circulated. About 900 new bitcoins are mined and put into digital circulation every day, but there could be more, as faster mining rates have led to rising mining rates.
As the halving continues, the rate of Bitcoin supply growth will slow until all 21 million BTC are mined. According to predictions, the last part of Bitcoin will be mined in 2140.
Payouts for mining the block will be halved again in the future, but no exact date has been set. The answer will be revealed when 210,000 blocks have been mined since the last halving.
With new Bitcoins mined every 10 minutes, the next halving is likely to occur in early 2024, at which point miner payouts will drop to 3.125 BTC.
Summary:
The Bitcoin halving is a highly publicized event that has occurred roughly every four years since the first occurred in 2012. Keeping the overall supply constant is part of the underlying programming of cryptocurrencies.
Further Readings:
Click on the below links to read relevant articles on cryptocurrencies.
FAQs
How long does it take to mine 1 Bitcoin?
around 10 minutes
What is Bitcoin halving date?
Bitcoin’s algorithm dictates halving based on the specific creation of blocks. No one knows exactly when the next halving will be, but experts say May 2024 is likely.
How often is Bitcoin halved?
roughly every four years
How many Bitcoin Halvings are left?
The halving takes about 10 minutes on average to mine the block, so the halving occurs about every 4 years. After a total of 64 halves, there are no more Bitcoins to reward miners, and all 21 million Bitcoins are in circulation. This will happen sometime in the year 2140.
What happens after the maximum number of bitcoins has been issued?
The final halving is expected to occur in 2140, after which block rewards will no longer be in the form of Bitcoin. In return, miners receive commissions from network users who buy and sell bitcoin, giving them the incentive to continue processing transactions on the blockchain.
Can I make money from the BTC halving?
Yes, you can make money from the BTC Halving by speculating on Bitcoin price movements in the weeks and months surrounding the event. Contracts for difference are a popular way to speculate on Bitcoin price movements. This allows you to go long or short.
However, it is important to remember that all forms of trading involve risk. So, while you have the chance to win, you shouldn’t risk more than you can afford to lose.
Does Bitcoin halving increase price?
Bitcoin’s halving is impacting its market value as more coins are released into the network and demand increases. This will lead rise to the value of coins increasing.
Should I buy Bitcoin during halving?
Halving generally results in cryptocurrency prices rising due to reduced supply and increased demand, which is good news for investors. In anticipation of the halving, trading activity on cryptocurrency blockchains is increasing.



